Enable Hyper-V to create virtual machines on Windows 10.
Hyper-V can be enabled in many ways including using the Windows 10 control panel, PowerShell or using the Deployment Imaging Servicing and Management tool (DISM). This documents walks through each option.
Note: Hyper-V is built into Windows as an optional feature -- there is no Hyper-V download.
Check Requirements
- Windows 10 Enterprise, Pro, or Education
- 64-bit Processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT).
- CPU support for VM Monitor Mode Extension (VT-c on Intel CPUs).
- Minimum of 4 GB memory.
The Hyper-V role cannot be installed on Windows 10 Home.
Upgrade from Windows 10 Home edition to Windows 10 Pro by opening up Settings > Update and Security > Activation.
For more information and troubleshooting, see Windows 10 Hyper-V System Requirements.
Enable Hyper-V using PowerShell
-
Open a PowerShell console as Administrator.
-
Run the following command:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V -All
If the command couldn't be found, make sure you're running PowerShell as Administrator.
When the installation has completed, reboot.
Enable Hyper-V with CMD and DISM
The Deployment Image Servicing and Management tool (DISM) helps configure Windows and Windows images. Among its many applications, DISM can enable Windows features while the operating system is running.
To enable the Hyper-V role using DISM:
-
Open up a PowerShell or CMD session as Administrator.
-
Type the following command:
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /All /FeatureName:Microsoft-Hyper-V
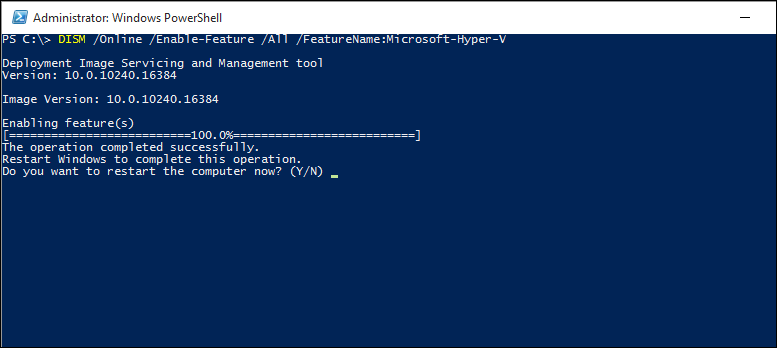
For more information about DISM, see the DISM Technical Reference.
Enable the Hyper-V role through Settings
-
Right click on the Windows button and select ‘Apps and Features’.
-
Select Programs and Features on the right under related settings.
-
Select Turn Windows Features on or off.
-
Select Hyper-V and click OK.
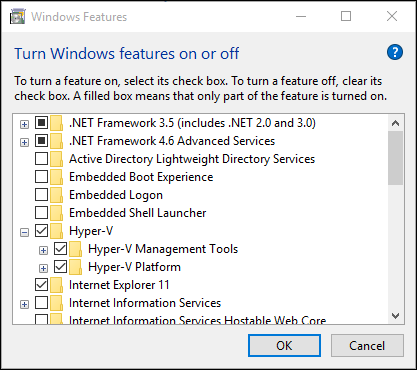
When the installation has completed you are prompted to restart your computer.
